The big data sector is rapidly expanding as a result of applications in a variety of domains such as Telecommunication, Healthcare, Retail, Banking, Manufacturing, Supply chain, and so on.
After firms have collected large amounts of data, the next critical step is to begin using advanced analytics. Big data analytics enables organizations to understand their customers’ needs and preferences in a better way. It allows them to expand their client base and retain existing customers through personalized and relevant product or service offerings.
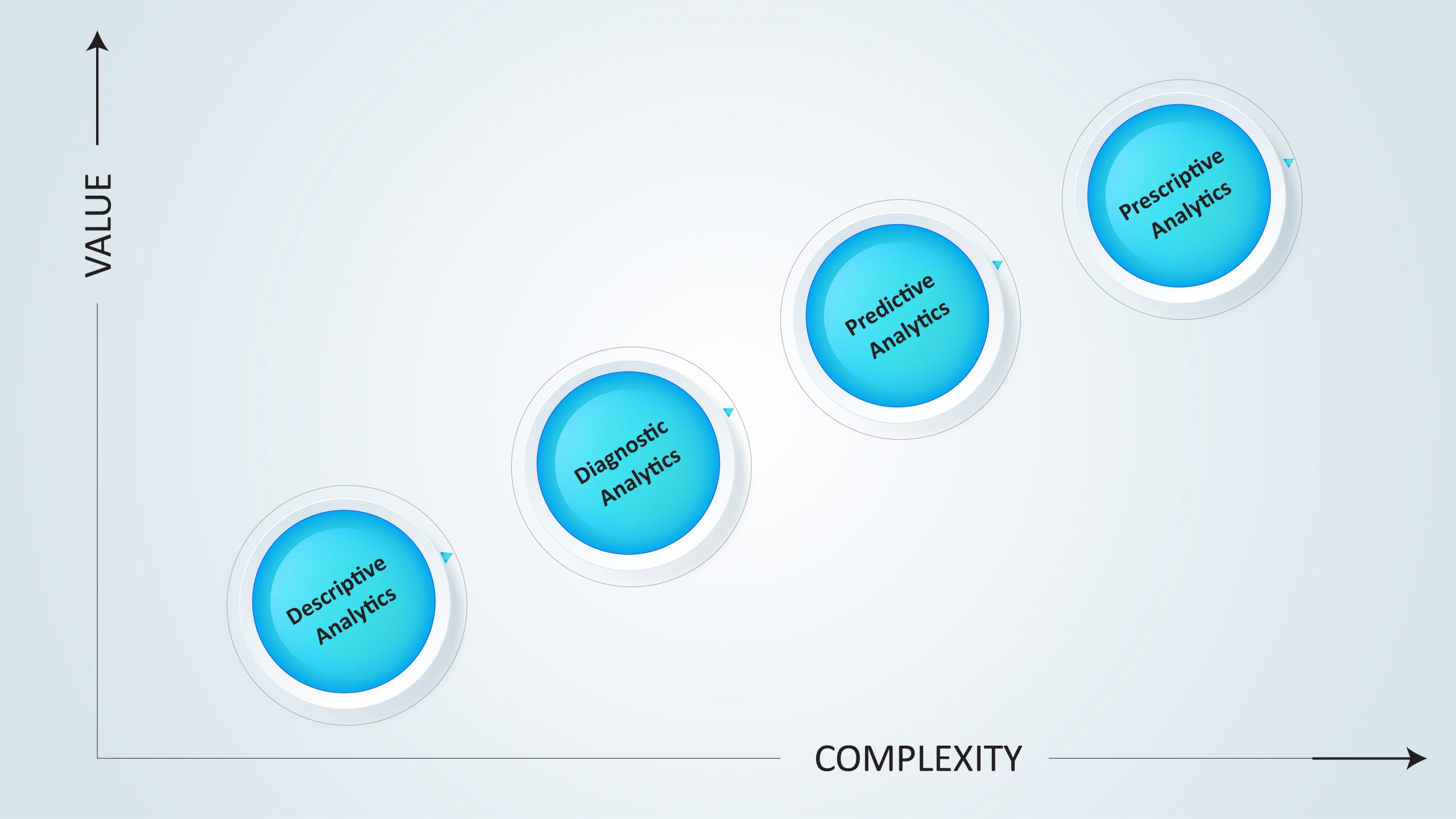
Many businesses are unsure where to start, what forms of analytics will help them expand, or what these various types of analytics represent. Let’s look at the various kinds of analytics and the value they add to a company.
Descriptive analytics
When a firm intends to know the overall performance of the organization at a high level, descriptive analytics is used. This is the most prevalent of all the different types. In business, it gives the analyst a glimpse of the company’s main indicators and KPIs.
The most basic definition of descriptive analytics is that it responds to the inquiry “What happened?”. This sort of analytics examines real-time and historical data to provide insights about how to proceed in the future. The basic goal of descriptive analytics is to figure out why things worked out or didn’t work out in the past. The ‘past’ here refers to any specific period when an event occurred, which could be a month or even a minute ago.
The results that a firm receives from the webserver using Google Analytics tools are the best example of descriptive analytics. Descriptive analytics is enhanced when effective visualization tools are used.
Advantages and limitations of descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics has a lot of benefits. Descriptive analytics does not require a thorough understanding of analytical or statistical methodologies, and it can be carried out using easily available resources. It can answer many of the most typical queries concerning business performance, such as whether sales were in line with expectations in the previous quarter. Thus, it can aid the company in identifying areas for improvement.
The main disadvantage of descriptive analytics is that it merely presents what has occurred rather than investigating the causes or attempting to forecast what will occur next.
Diagnostic analytics
Diagnostic analytics will enable an analyst to go down and find the root cause of an issue based on the descriptive data. Such analysis is possible with well-designed business information (BI) dashboards that incorporate the reading of time-series data (data spanning numerous consecutive points in time) and include filters with drill-down functionality.
Diagnostic analytics figures out “why” something happened. Businesses utilize this type of analytics to gain a deep understanding of a problem if they have enough data at their reach. Diagnostic analytics aids in the detection of anomalies in data. For example, eCommerce heavyweights like Amazon can pull out sales and gross profit per product category, such as Amazon Echo, to determine why they fell short on total profit margins.
Advantages and limitations of descriptive analytics
Companies can gain significant insights into their prospects and difficulties by utilizing them. Diagnostic Analytics enables businesses to turn complex data into easily manageable and understandable information, which is presented in the form of visualizations and insights that anyone can understand.
Businesses may remove ambiguity in decision-making by knowing where they are in the market and having a clear view of their business landscape. As a result, they are able to make better-informed judgments, improve response rates, and optimize their business overall.
One of the drawbacks of this sort of analytics is that it focuses on past events, limiting its capacity to deliver useful future insights. When looking for relevant insights, they must use other techniques like predictive analytics and prescriptive analytics, which identify possible future events.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics is a form of advanced analytics that uses historical data, statistical modeling, data mining techniques, and machine learning to create predictions about future outcomes. Predictive analytics is used by businesses to uncover trends in data and identify threats and opportunities.
Forecasting is at the core of predictive analytics. Predictive models are used to determine the likelihood of an event occurring in the future, anticipate a quantifiable amount, or estimate a point in time when something might occur.
The ability to “predict” what might happen is at the heart of predictive analytics. Understanding the future is the goal of these analyses. Being able to forecast assists one to make better decisions in a world when there is so much uncertainty. Predictive models are widely used in many fields such as telecommunication, health care, retail, supply chain, and so on.
Advantages and limitations of predictive analytics
Predictive analytics can be used to influence upselling, sales and revenue forecasting, manufacturing optimization. These techniques can guide managers and executives with decision-making processes for future events.
In Predictive analytics, data quality is important. Most of the time, companies collect data which are not reliable. For example, not everyone will tell you the truth about how many times they exercise or how many alcoholic beverages they have each week. People may not be intentionally dishonest, but the data is still distorted.
Prescriptive analytics
The prescriptive model employs an understanding of what has occurred, why it has occurred, and a range of “what-might-happen” analyses to assist the user in identifying the appropriate course of action. Prescriptive analytics has been used by many advanced data analytics companies to maximize the customer experience by scheduling inventory in the supply chain, improving production, and so on.
According to Gartner(1), the market for prescriptive analytics software will grow at a rate of 20.6 percent between 2017 and 2022. This indicates that approximately 37% of businesses will begin to use prescriptive analytics.
Advantages and limitations of prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics gives firms advice on all possibilities and leads to actions that are most likely to increase business outputs. The Prescriptive analytics approach provides insights into “what should a business do” to solve an issue. This method enables organizations to make decisions in the face of uncertainty.
The quality of the input variables and data determines the insights received. Overfitting in prescriptive models, for example, can result in faulty forecasts that are immune to changes in data over time, while missing or wrong information can lead to false predictions.
Despite its uses in several domains, Prescriptive Analytics’ capabilities are restricted. These restrictions are imposed by company restraints such as budget and other factors.
Conclusion
It’s essential to note the types of analytics and how they interact as you begin your analytics journey. Starting with Descriptive Analytics to figure out what happened, then moving on to Diagnostic Analytics to figure out why it happened. Once this is done, a Predictive analysis will be used to predict what will happen next, and Prescriptive Analytics can be used to indicate the best next steps to take.
Thus, it is necessary to know the types of analytics and how they can contribute to your business which will help you to get better results.